Understanding NVQ Level 4 in Construction Site Supervision
What is the NVQ Level 4 Qualification?
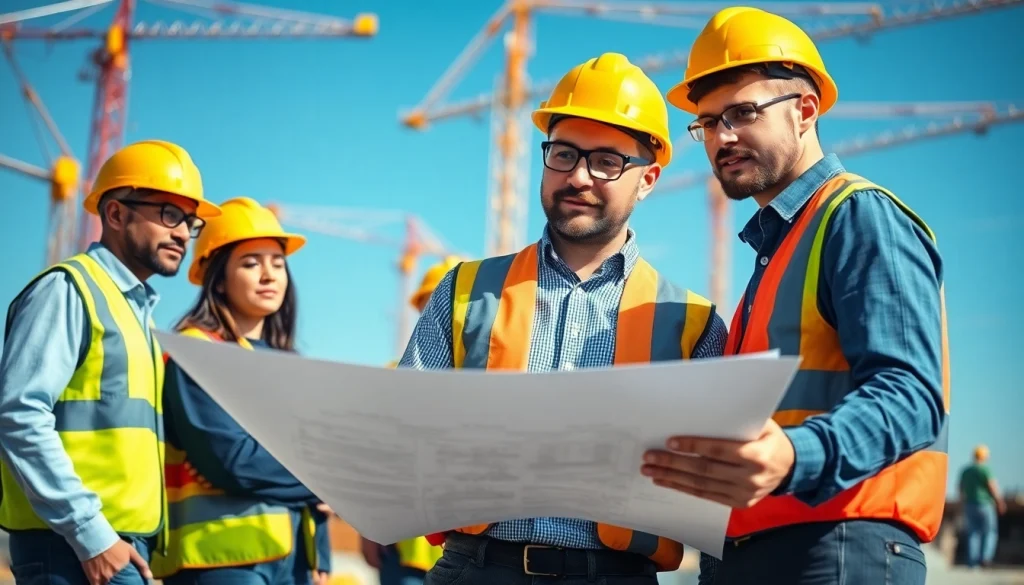
The NVQ Level 4 Qualification in Construction Site Supervision is a vital stepping stone for individuals seeking to enhance their competencies in the construction industry. This qualification is tailored for those who are responsible for overseeing the day-to-day operations on construction sites and ensuring that projects conform to relevant laws, regulations, and company standards. It covers critical areas such as health and safety, personnel management, project management, and business practices, equipping candidates with the knowledge and skills necessary to handle complex supervisory roles.
Key Learning Outcomes for Supervisors
The primary learning outcomes for candidates pursuing the NVQ Level 4 in Construction Site Supervision include understanding and effectively implementing health and safety regulations, managing a team, and developing strong communication skills. Supervisors also learn to assess and mitigate risks, oversee site activities, and ensure quality control in all project phases. This qualification emphasizes practical application, enabling candidates to demonstrate their abilities in their current roles.
Common Challenges Faced by Candidates
Many candidates encounter various challenges while pursuing the NVQ Level 4 certification. These challenges include understanding the assessment process, finding opportunities to demonstrate competence on site, and gathering sufficient evidence for their portfolios. Additionally, they may struggle with time management as they balance work commitments with study and assessment preparation. Proper guidance and structured study plans can help mitigate these issues and lead to successful outcomes.
Essential Answers for NVQ Level 4 Construction Site Supervision
Sample Questions and Expert Responses
As part of the NVQ Level 4 assessment, candidates may face a range of questions that challenge their understanding of supervision in construction. For example:
- What are the key responsibilities of a construction site supervisor?
A construction site supervisor is responsible for managing site operations, ensuring compliance with health and safety regulations, coordinating the workforce, and maintaining quality standards. - How do you implement health and safety measures effectively on-site?
Effective implementation involves performing risk assessments, conducting safety training, and ensuring that all staff are aware of safety protocols and emergency procedures.
Mandatory vs Optional Units Explained
The NVQ Level 4 certification consists of both mandatory and optional units, providing flexibility for candidates to tailor their studies according to their specific roles in construction. Mandatory units typically cover essential content necessary for all supervisors, such as:
- Health and Safety Management
- Quality Control
- Project Planning and Organization
Optional units allow candidates to specialize in areas most relevant to their job, such as:
- Environmental Management
- Resource Management
- Contract Management
Effective Study Strategies for Success
To excel in the NVQ Level 4 Construction Site Supervision qualification, candidates should adopt effective study strategies. These might include:
- Creating a Study Plan: Outline a schedule that allocates specific times for study, reflection, and practice.
- Using Past Papers: Familiarize yourself with the types of questions that may appear on assessments and practice your responses.
- Participating in Study Groups: Collaborate with peers to discuss complex topics and share insights, fostering a deeper understanding of subject material.
Health, Safety, and Welfare in Construction
Importance of Safety Protocols
Health, safety, and welfare are paramount in the construction industry, necessitating rigorous adherence to protocols. The implementation of safety measures not only protects workers but also ensures project efficiency and continuity. A safe work environment minimizes the risk of accidents and enhances overall morale among team members. Supervisors play a pivotal role in establishing a culture of safety, which begins with thorough training and constant vigilance.
Implementing Safety Standards Effectively
Effectively implementing safety standards requires proactive measures, including the development of safety policies, regular site inspections, and ongoing training for all personnel. Supervisors should lead by example, highlighting the importance of following safety procedures and encouraging employee participation in safety discussions. Additionally, the use of technology, such as digital safety checklists and monitoring systems, can enhance compliance and reporting.
Tools for Monitoring Workplace Safety
Various tools and methodologies can assist supervisors in monitoring workplace safety. These include:
- Safety Audits: Regularly conducting audits can help identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety protocols.
- Incident Reporting Systems: Implementing systems for reporting accidents or near misses can help in understanding risks and preventing future occurrences.
- Training Management Software: Utilizing software to track training compliance can ensure that all team members have the required safety credentials.
Building Strong Working Relationships
Communication Skills for Supervisors
Strong communication skills are essential for successful site supervision. Supervisors must effectively convey information to their teams, ensure that instructions are clear, and foster open dialogue among all workers. Techniques to enhance communication include active listening, providing constructive feedback, and employing motivational communication strategies that encourage participation and commitment from team members.
Enhancing Team Collaboration
Collaboration among team members is crucial for project success. To enhance this, supervisors can implement team-building exercises both on-site and off-site, which help to build trust and improve relationships among workers. Additionally, using collaborative project management tools can facilitate smoother communication and coordination among various parties involved in the construction process.
Conflict Management Techniques
Conflicts may arise on construction sites due to various factors, ranging from personality clashes to misunderstandings. Effective supervisors should be equipped with conflict management techniques, which may include:
- Active Listening: Understanding the perspectives of all parties involved can help de-escalate conflicts.
- Problem Solving: Encouraging team members to collaborate on solutions fosters a sense of ownership and accountability.
- Mediation: Act as a neutral party to facilitate discussions and guide conflicting individuals toward a resolution.
Preparing for Your Assessment
What to Expect During the Assessment Process
The assessment process for the NVQ Level 4 qualification can vary depending on the assessment center, but generally includes two main components: the submission of a portfolio and an observation at the workplace. Candidates should prepare for both aspects by gathering evidence of their work, such as completed projects, safety records, and feedback from peers or clients. Understanding the specific requirements set by the assessor can also streamline preparation efforts.
Gathering Evidence for NVQ Assessments
Gathering evidence is a critical step in the NVQ Level 4 assessment process. Candidates should focus on collecting diverse types of evidence that showcase their skills and knowledge. Examples include:
- Photographs of work completed.
- Witness statements from colleagues or clients.
- Records of completed training and certificates.
Organizing this evidence in a comprehensive portfolio can help demonstrate a candidate’s competency across the required standards effectively.
Post-Assessment Steps and Continuous Improvement
Upon completion of the assessment, candidates should engage in continuous improvement practices. This might involve reflecting on feedback received during the assessment, setting professional development goals based on areas for enhancement, and pursuing further education or training. Engaging in regular professional development activities increases skill proficiency and ensures one remains competitive within the industry.
For comprehensive assistance with the NVQ Level 4 qualification, including detailed answers to a variety of critical topics, explore our resource on NVQ Level 4 Construction site supervision answers.